Top 8 Critical Thinking Skills for Students
Critical thinking skills foster intellectual growth and prepare students for real-world challenges. They enable students to assess situations objectively and make reasoned decisions.
Experts like Michael Scriven and Richard Paul define critical thinking as the disciplined process of gathering, analyzing, and evaluating information from various sources and using that information to guide belief and action. This article explores the top eight critical thinking skills for students and strategies for developing them.
Key Critical Thinking Skills for Students
Critical thinking skills for students encompass several vital skills, each uniquely impacting a student’s intellectual development.
1. Problem-solving
Problem-solving requires students to identify challenges, develop potential solutions, evaluate those options, and implement the best one. This skill applies to various areas, from coursework to everyday decision-making.
Key elements of problem-solving include:
- Defining the problem clearly and precisely
- Collecting relevant information for analysis
- Brainstorming various possible solutions
- Assessing the advantages and disadvantages of each solution
- Executing the most effective solution and tracking its impact
Example: A school project leader assesses conflicting ideas from group members and devises a compromise that incorporates all viewpoints while meeting the project’s requirements.
2. Analytical Thinking
Analytical thinking allows students to break down intricate information into smaller, digestible parts. It enables them to identify trends, patterns, and cause-and-effect relationships while objectively analyzing data. This skill helps students remain impartial and base their conclusions on evidence rather than assumptions.

Key aspects of analytical thinking include:
- Recognizing patterns and trends within information
- Identifying the causes and consequences of specific actions or events
- Evaluating the strength and validity of arguments and supporting evidence
Example: A student managing the school’s social media account examines the engagement data from various posts and uses it to develop a strategy for improving interactions with followers.
3. Open-mindedness
Open-mindedness is the ability to approach new ideas and viewpoints with an unbiased perspective. This skill helps students evaluate information objectively, particularly in collaborative environments where different perspectives are shared.

Key qualities of open-mindedness include:
- Considering diverse viewpoints and alternative ideas
- Welcoming constructive feedback and criticism
- Adjusting one’s beliefs and ideas when presented with new, credible information
Example: In a group project, a student team leader listens attentively to a new team member’s unconventional suggestion and incorporates it into their final project plan, resulting in a creative and effective outcome.
4. Communication
Communication is essential for clearly expressing ideas and understanding others’ perspectives. Strong communication skills help students present complex concepts, listen actively, and respond thoughtfully.

Key components of communication in critical thinking skills for students include:
- Articulating ideas clearly and effectively
- Adjusting communication style based on the audience
- Presenting logical, persuasive arguments in both written and spoken formats
Example: A student explains their research findings in a science project, using visual aids and simple language to ensure the audience grasps the main concepts.
5. Research
Research skills allow students to gather, evaluate, and synthesize information from various sources. Critical thinking enhances students’ ability to identify reliable sources, assess their credibility, and build a well-supported argument.

Key components of research include:
- Locating reliable and relevant sources of information
- Assessing the credibility and potential bias of sources
- Integrating information from multiple sources into a cohesive argument
Example: A high school student writing a research paper on climate change gathers credible articles, scientific reports, and case studies from academic sources to support their argument about the impact of global warming on local ecosystems.
6. Decision-making
Decision-making involves evaluating different options, considering possible outcomes, and selecting the best course of action. It requires logical analysis and thoughtful consideration of consequences.

Key aspects of decision-making include:
- Establishing clear criteria for evaluating different options
- Weighing short-term and long-term consequences
- Balancing logical analysis with intuitive reasoning
Example: A student planning a school event weighs the pros and cons of hosting it indoors or outdoors, considering factors like weather, space, and accessibility before deciding.
7. Reasoned Judgment
Reasoned judgment involves making informed decisions by carefully analyzing evidence and considering multiple perspectives. It requires objectivity and the ability to assess the credibility and relevance of different viewpoints before concluding.

Key elements of reasoned judgment include:
- Gathering and evaluating information objectively
- Assessing the reliability and significance of evidence
- Drawing logical conclusions based on sound reasoning
Example: While working on a group project, students listen to their peers’ suggestions and evaluate the feasibility of each idea based on time constraints, resources, and learning objectives, ensuring the group makes a practical decision.
8. Reflective Thinking
Reflective thinking encourages students to evaluate their thought processes and decision-making strategies. By reflecting on past experiences, students can identify areas for improvement and make better decisions in the future.

Key aspects of reflective thinking include:
- Examining personal assumptions and biases critically
- Integrating knowledge from different sources and past experiences
- Applying insights gained through reflection to improve future actions
Example: After completing a difficult math exam, students reflect on their study habits, recognize areas for improvement and adjust their preparation strategy for future tests.
How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills for Students
Developing critical thinking skills for students is an ongoing process that requires deliberate effort and practice.
- Encourage Questioning and Curiosity: Promoting inquiries like “What if…” or “Why does this happen?” helps deepen their engagement and critical thinking.
- Provide Real-World Contexts for Learning: Practical situations like budgeting can illustrate the relevance of math teaching.
- Promote Active Listening Skills: Encourage students to practice active listening to understand diverse perspectives and refine their views.
- Foster Collaborative Learning Environments: Facilitate group activities that promote sharing and discussion, enhancing diverse thinking.
- Create Space for Reflection: Allow students to reflect on their ideas, question their assumptions, articulate their beliefs, and thoughtfully consider others’ perspectives.
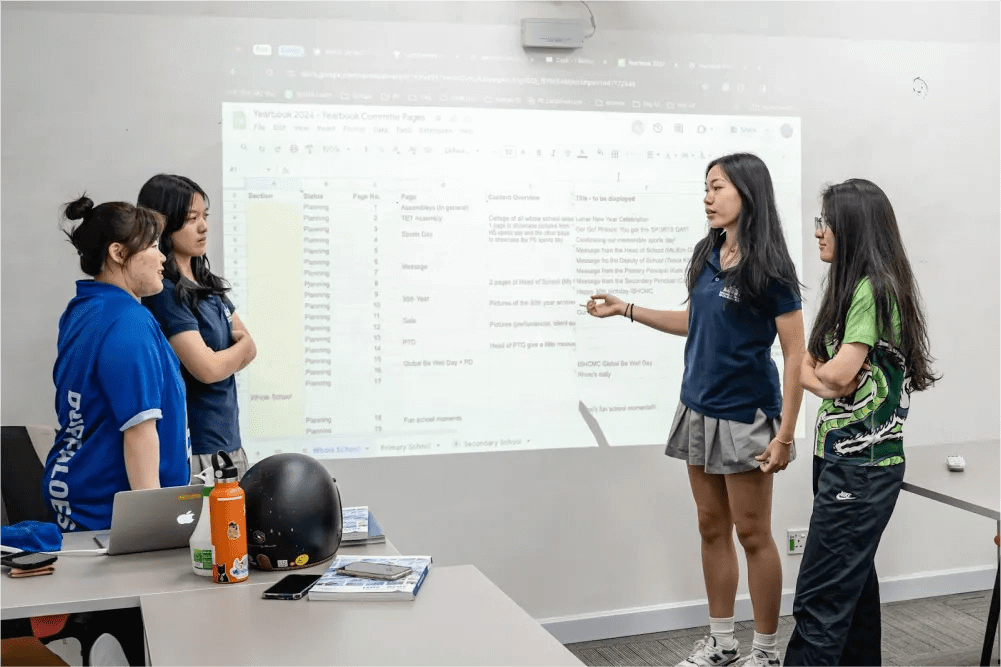
At the International School Ho Chi Minh City (ISHCMC), we prioritize developing critical thinking skills for students through the International Baccalaureate (IB) program. The IB curriculum challenges students to think critically and engage with diverse perspectives, preparing them for success in an interconnected world.

Through inquiry-based learning, ISHCMC encourages students to take ownership of their education, ask insightful questions, and apply their knowledge to real-world problems. Our programs emphasize research, reflection, and collaboration, ensuring students excel academically and grow as responsible, global citizens.
Develop Critical Thinking Skills with ISHCMC’s IB Education
At ISHCMC, we recognize the importance of fostering critical thinking skills for students as they prepare for a dynamic future. Our IB curriculum provides a unique platform where students can learn how to question assumptions, evaluate evidence, and make informed decisions. Focusing on inquiry-based learning and global awareness, we prepare students for success in their academic and personal lives.

Explore the opportunities that await at ISHCMC and experience firsthand our supportive and enriching learning environment. Apply today and take the first step toward empowering your child’s educational journey!